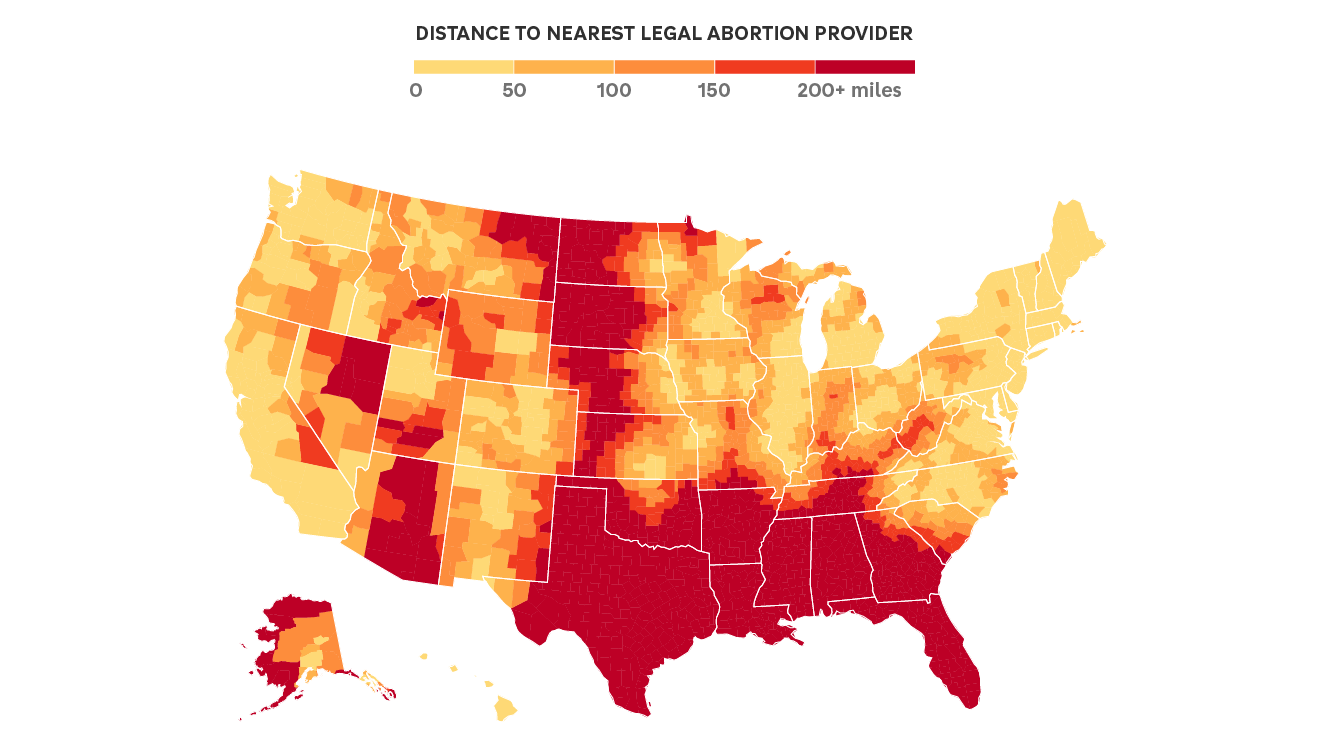
In a few weeks, Florida and Arizona are set to join most states in the southern U.S. in banning abortion. It’s a significant shake up to the abortion legal landscape, and data shared exclusively with NPR maps and quantifies what the changes will mean for millions of Americans.
On Tuesday, the Arizona Supreme Court cleared the way for an 1864 law to be enforced. That law completely bans abortion except when someone’s life is in danger. Last week, the Florida Supreme Court made its decision to allow a ban on abortions after six weeks gestation to take effect on May 1.
Caitlin Myers, an economics professor at Middlebury College in Vermont, has been tracking abortion facilities and travel distances since 2009. She analyzed how these latest rulings will affect the access map.
“Because of these bans, it’s about 6 million women of reproductive age who are experiencing an increase in distance of more than 200 miles,” she says.
She points out that Floridians who are seeking abortions after six weeks will have to travel nearly 600 miles to North Carolina, which has a 72-hour waiting period. “So we’re talking about a day’s drive to a state that requires you to engage in this multi-day process,” Myers says. “A lot of people might end up going several hundred miles further to Virginia.”
For people in Arizona, after the 1864 law takes effect, “their nearest destinations are pretty long drives. They’re going to be facing hundreds of miles to reach southern California, New Mexico, Colorado,” Myers says. “I think Arizona spillover is likely to affect California in a way that California hasn’t yet been affected by bans.”
Myers helms the Myers Abortion Facility Database. She has gathered data about facilities – including clinics, doctors, and hospitals that publicly indicated that they provide abortions – going back more than a decade, using data licensure databases, directories, and Wayback Machine captures of websites from years past. She uses a team of undergraduate research assistants to periodically call facilities and make sure the information is up to date.
Numbers of abortions rise in Florida, decline in Arizona
Although Florida and Arizona have historically both been politically purple states and both have had 15-week abortion bans since 2022, the states have been on different trajectories when it comes to abortion and play very different roles in their regions.
There were about 12,000 abortions in Arizona in 2023, according to the Guttmacher Institute, a research organization that supports abortion rights. Out-of-state travel accounted for 3% of abortions in the state, and the overall number of abortions has been declining there in recent years, Guttmacher finds.
By contrast, there were nearly 85,000 abortions in Florida in 2023, according to state data, just a few thousand fewer than Illinois, which has positioned itself as a haven for people seeking abortions in the post-Roe era. And the number of abortions happening in the state has been on the rise. “The majority of the increase has been driven by out-of-state travel into Florida because of bans in surrounding states,” explains Isaac Maddow-Zimet, a Guttmacher data scientist. “That really speaks to the role that Florida has played in the region where there really aren’t many other options.”
The Alliance Defending Freedom, which brought the case in Arizona, frames those affected by the new laws in a different way. “We celebrate the Arizona Supreme Court’s decision that allows the state’s pro-life law to again protect the lives of countless, innocent unborn children,” the organization wrote in a statement this week.
Even with new bans in place, there are a few ways residents of Florida and Arizona will be able to access abortion without driving hundreds of miles. People with means will be able to fly to states where abortion access is protected. Others will be able to use telehealth to connect with providers in those states and receive abortion medication in the mail – a practice that has been growing in popularity in recent months. Telehealth medication abortions, though, could be curtailed by a pending case before the U.S. Supreme Court. (A decision in that case is expected this summer.)
In Florida, some will be able to get abortions before the six-week gestational limit, which is about two weeks after a missed period. “Folks have a really narrow window in order to meet that gestational duration limit if they even know about their pregnancy in time,” Maddow-Zimet of Guttmacher explains. “And that’s something that’s particularly difficult in Florida because Florida requires an in-person counseling visit 24 hours before the abortion.”
‘A substantial barrier’
Many thousands of people in Florida and Arizona will be unable to navigate those options and will carry their pregnancies instead, Myers says.
“It’s easy to think – if an abortion is so important to somebody, they will find a way, they will figure it out,” she says, but research on people seeking abortions illustrates why that’s not always possible. “[Many] are low income. They’re in very difficult life circumstances. They’re experiencing disruptive life events like the loss of a job or breaking up with a partner or threatened eviction. Many of them are parenting and have difficulty obtaining child care.” One large study showed about 80% of people seeking abortions had subprime credit scores.
“If you think about all that, it is perhaps not so surprising that the results of my research and other people’s research shows very strongly and unequivocally that distance is a substantial barrier to people who are seeking abortions,” Myers says.
Mary Ziegler, a law professor and historian of reproductive rights at the University of California – Davis, says it’s worth noting how these states both came to have new bans. “The common denominator is conservative state supreme courts reaching decisions contrary to what voters would want, interestingly, in an election year when those judges are facing retention elections,” she says.
Voters in Florida will have a chance to weigh in on abortion access in November, when an amendment to their state constitution will be on the ballot. An effort to put an abortion amendment on the ballot in Arizona is also underway. Abortions rights opponents in both states have pledged to fight the measures.